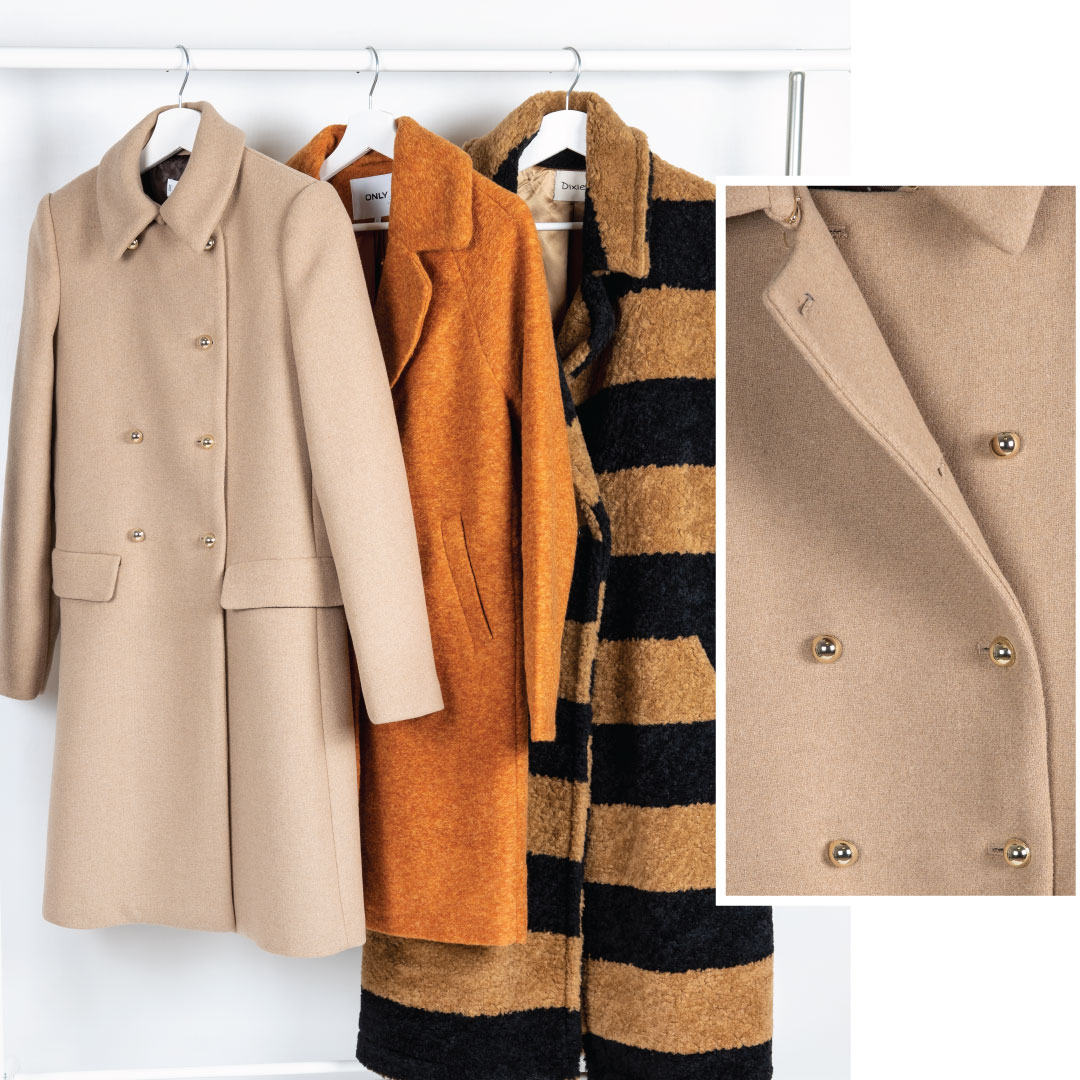
Hugo Boss Kaputi Online Srbija - BOSS Trench coat in stretch fabric with pepita check Ženske - Patterned
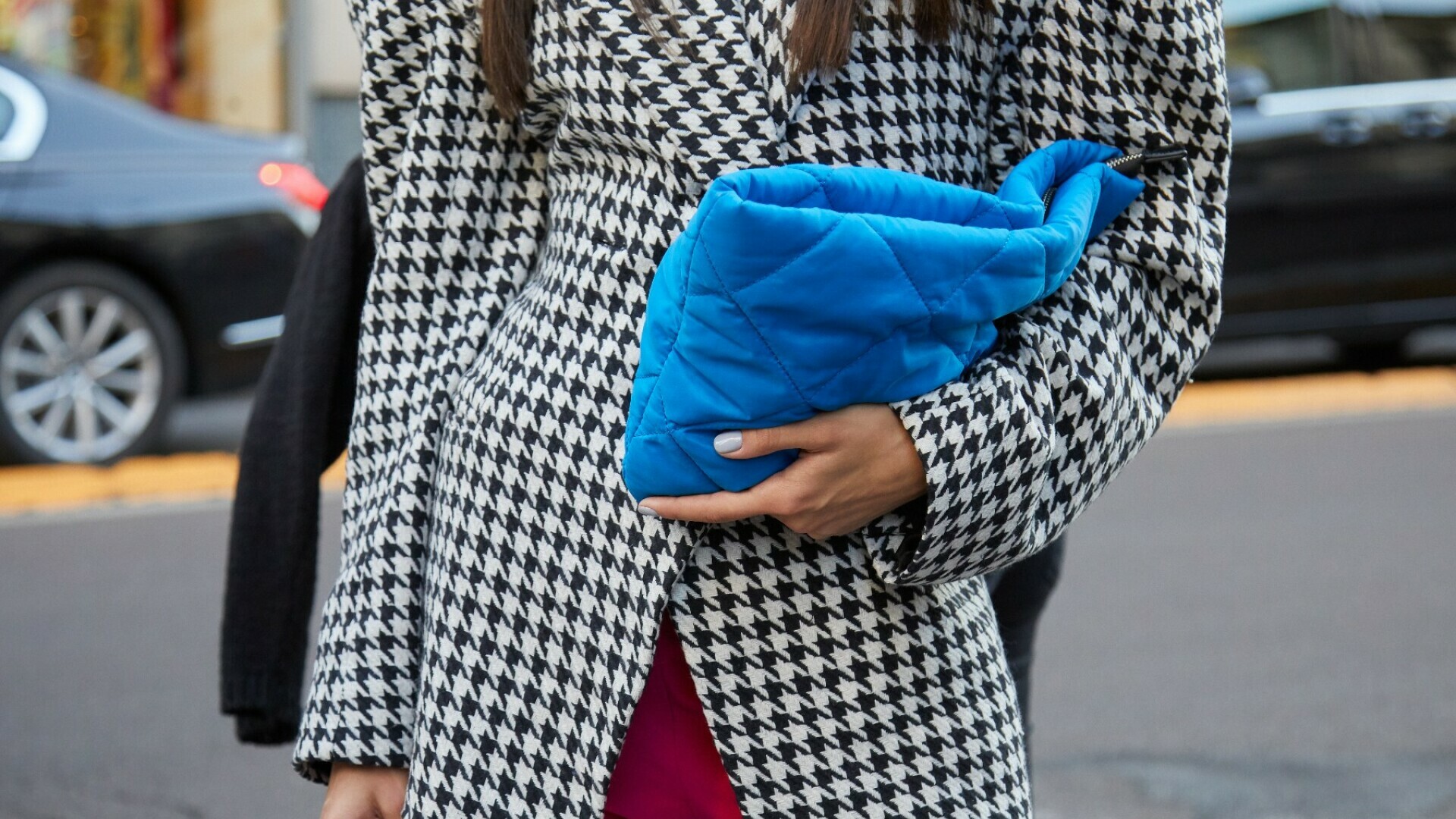

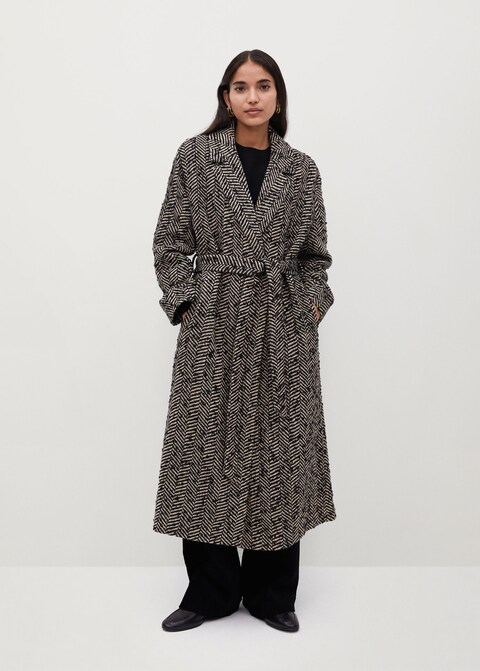
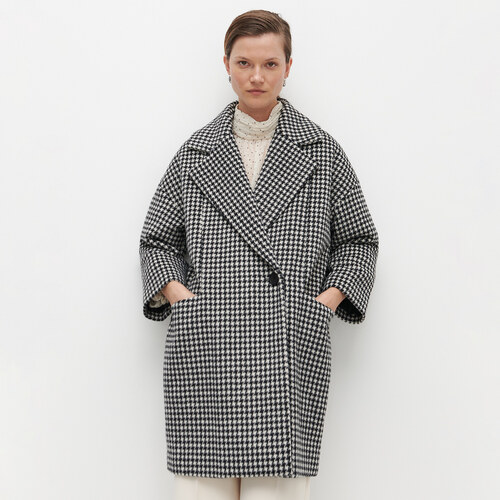
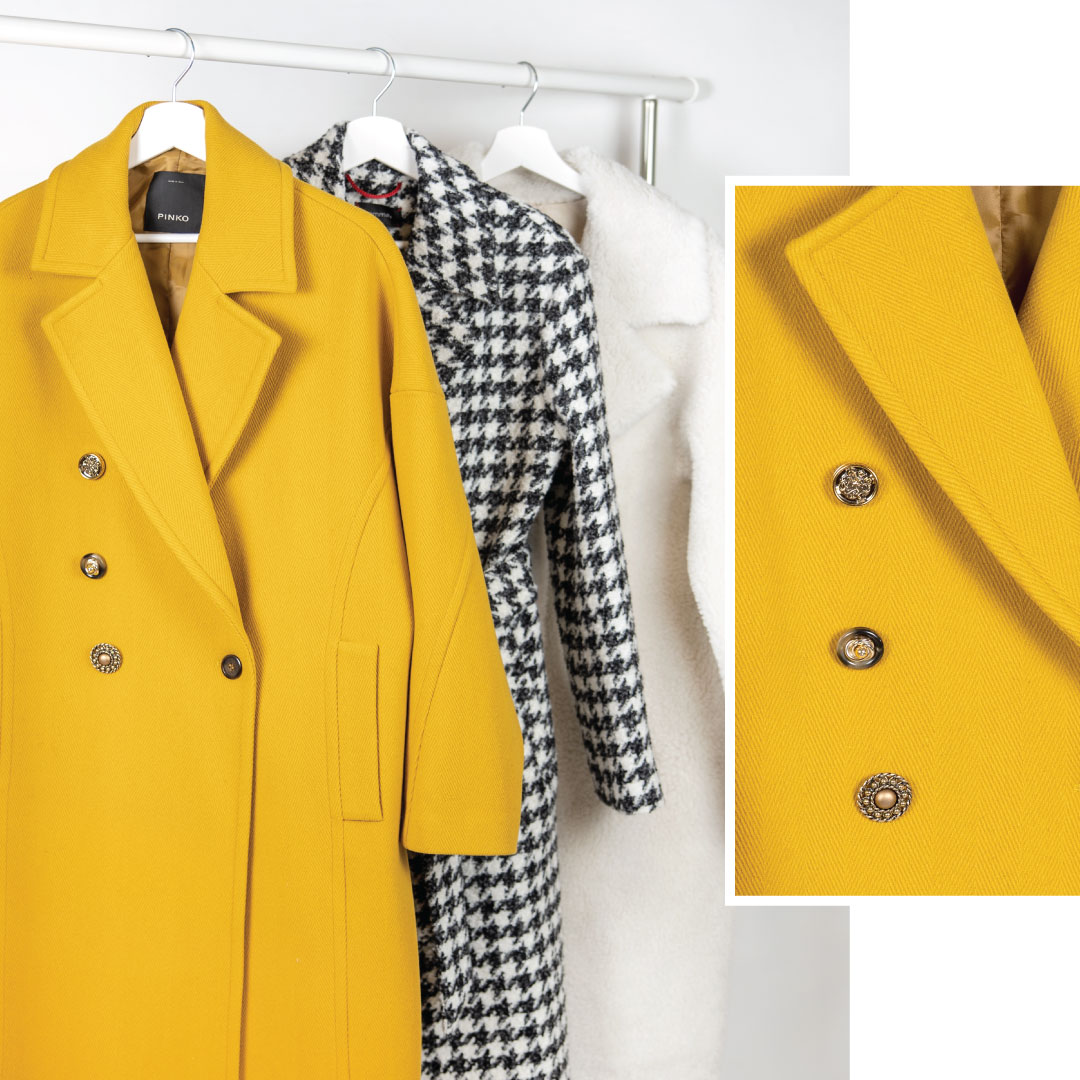
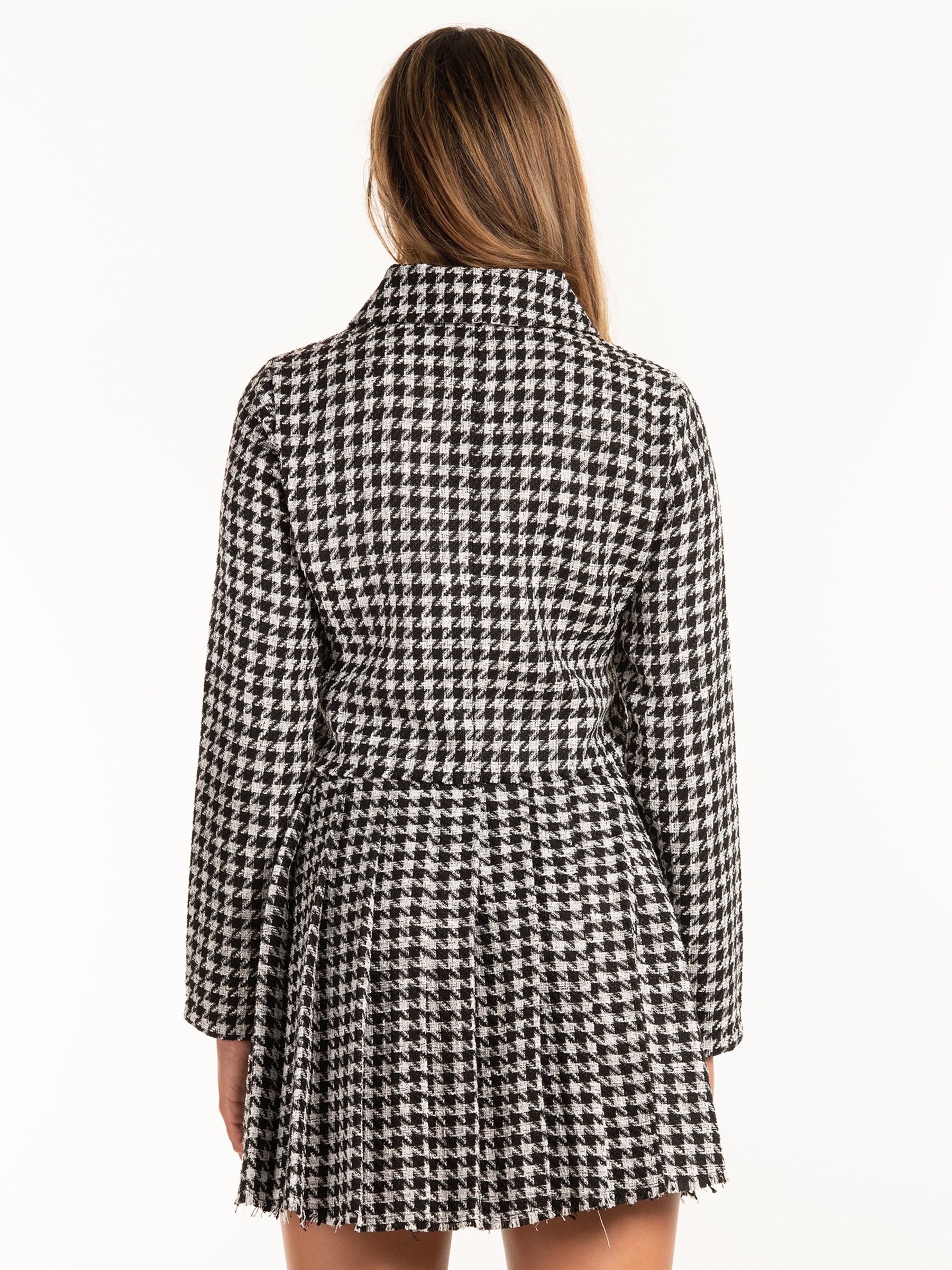
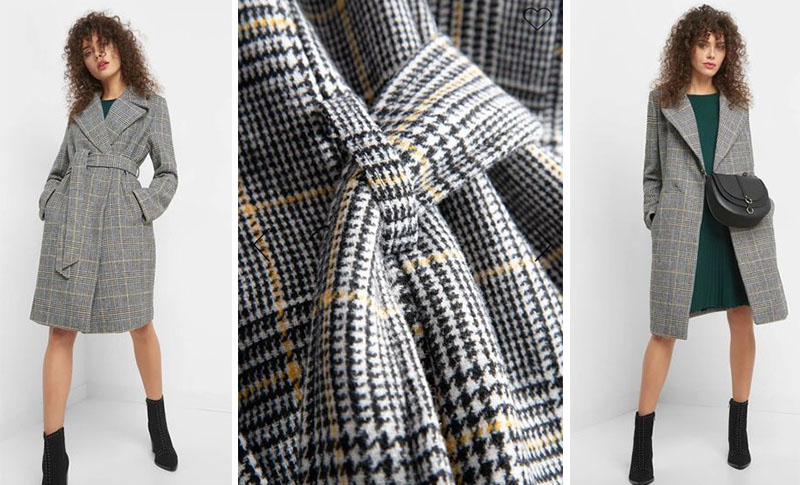
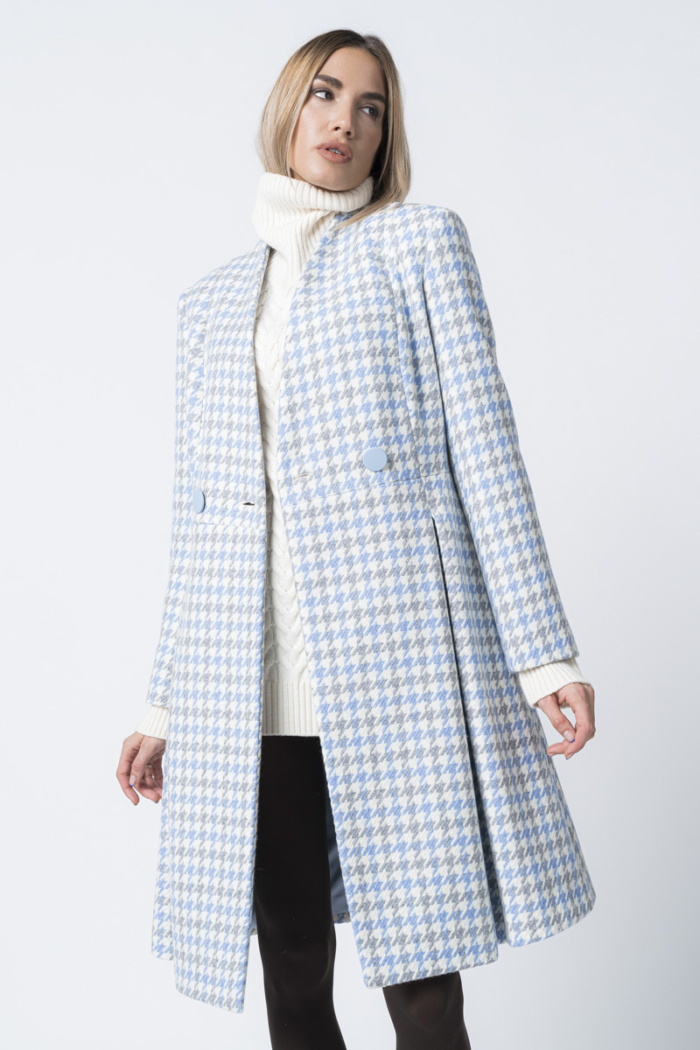
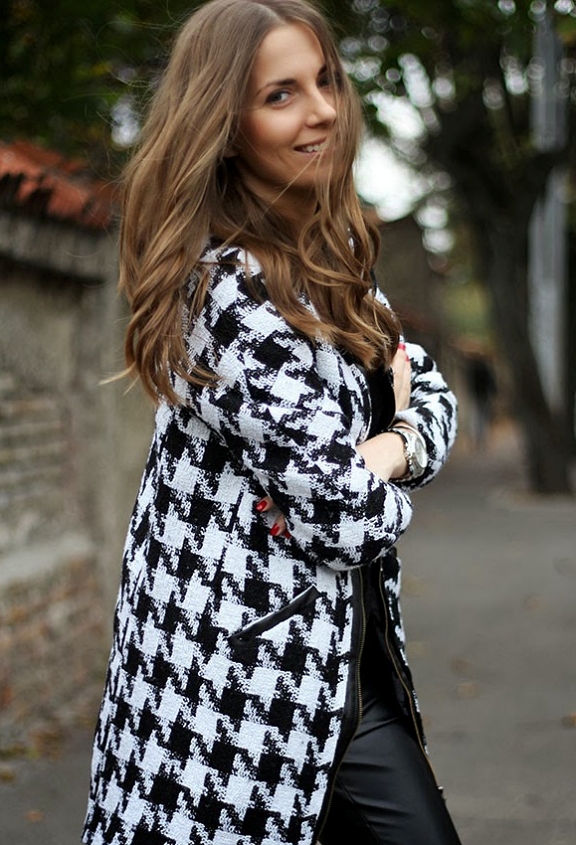
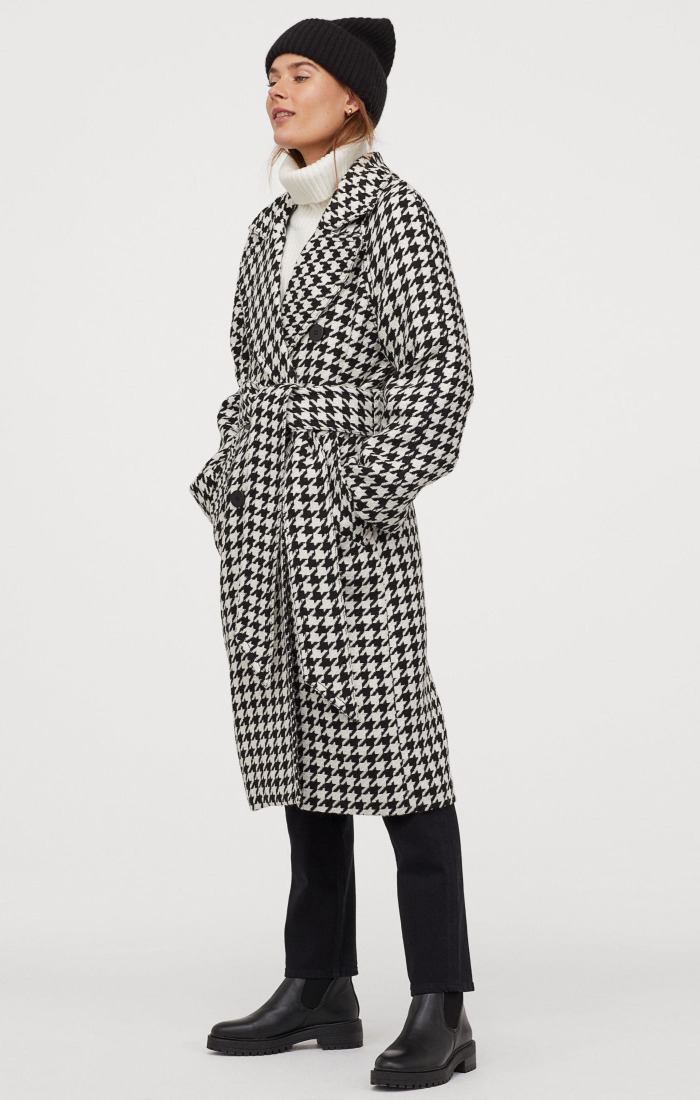
Suknje, haljine, kaputi, pletivo... 13 komada s pepita uzorkom uz koji svaka kombinacija izgleda više šik

Suknje, haljine, kaputi, pletivo... 13 komada s pepita uzorkom uz koji svaka kombinacija izgleda više šik